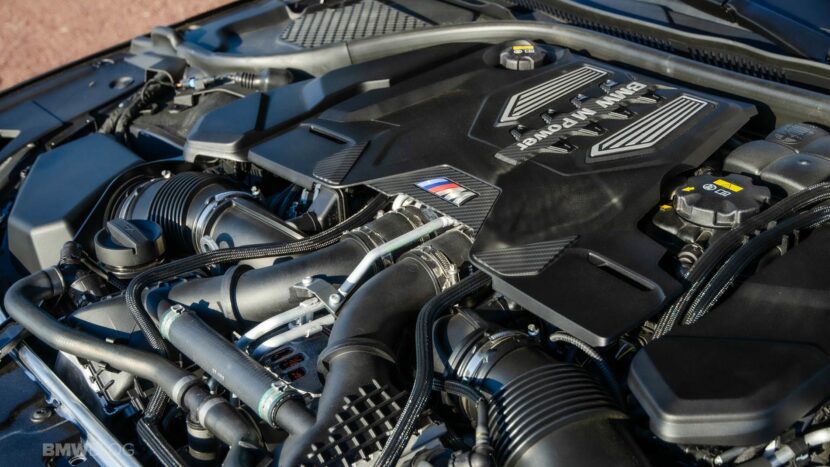
The BMW S63 engine is a high-performance, twin-turbocharged 4.4 liter V8 that has powered a range of BMW M models since its debut in 2010. Found in vehicles like the F10 M5, F12/F13 M6, F91/92/93 M8, F95 X5 M, and F96 X6 M, the S63 is known for its impressive performance, sound and tuning potential. The S63 features two twin-scroll turbochargers paired with a pulse-tuned, cross-engine exhaust manifold, designed to ensure a continuous flow of exhaust pulses to the turbochargers with every 180-degree crankshaft rotation. However, like any high-performance engine, it comes with its own set of reliability considerations and maintenance requirements.
Reliability of the S63 Engine
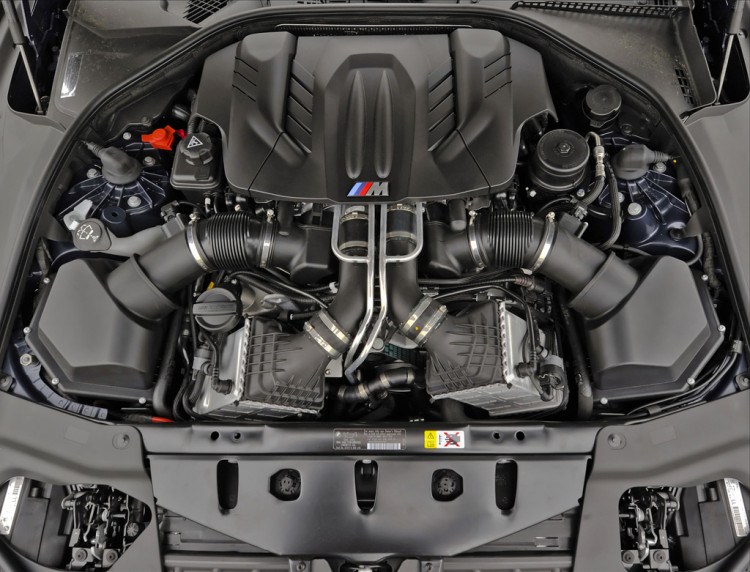
The BMW S63 V8 engine has evolved through several iterations, improving in power output and efficiency while addressing common issues identified in earlier versions. But of course, reliability often depends on proper maintenance and how the engine is used. Early versions of the S63 engine experienced issues such as rod bearing wear, turbocharger failures, valve stem seal wear, and cooling system weaknesses.
Common Issues:
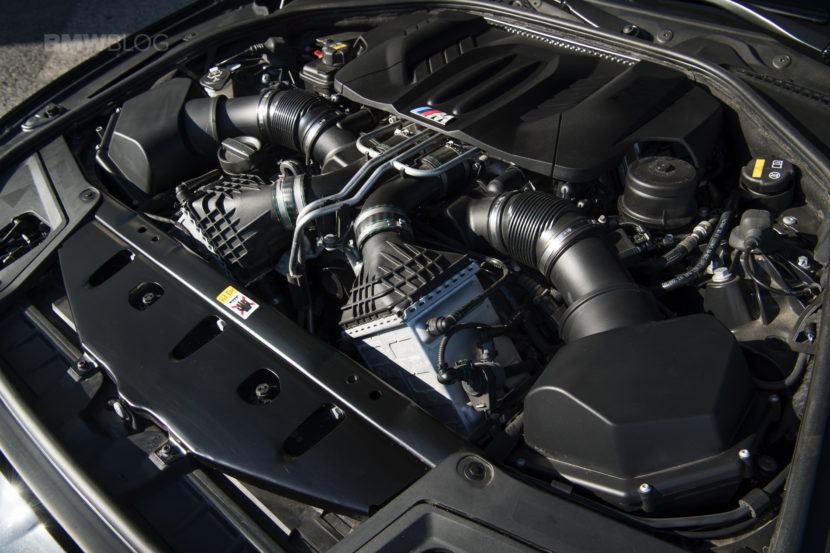

- Rod Bearing Wear: A known issue in early S63 engines, particularly in high-performance applications. Rod bearings can wear prematurely if not properly maintained or subjected to repeated high-RPM use.
- Turbocharger Failures: The S63’s twin turbos operate under high stress. Oil starvation or contamination can lead to turbocharger failures, particularly in engines with neglected oil changes.
- Valve Stem Seal Wear: Over time, worn valve stem seals can cause oil consumption issues, particularly in engines with higher mileage.
- Ignition Coil Failures: High-performance turbocharged engines like the S63 place significant stress on the ignition system, leading to coil failures over time. A single failed coil often signals that others will follow. Symptoms include misfires, rough idling, and reduced power. Regular checks can help prevent these issues and ensure consistent engine performance
- Excessive Oil Consumption: Early versions of the related N63 engine were notorious for excessive oil consumption due to issues like piston ring failure, leaking turbo seals, and valve stem seal wear. These problems were addressed in later designs, making them less common in the S63.
- Cooling System Weaknesses: The high thermal load of the S63 necessitates an efficient cooling system. Weak points like water pumps or radiators can cause overheating if not addressed.
Maintenance Requirements

- Frequent oil changes with high-quality synthetic oil are critical to maintaining turbocharger and engine health.
- Regular inspection of the cooling system and replacement of coolant at specified intervals is necessary to avoid overheating.
- Periodic replacement of spark plugs and coils ensures optimal performance and avoids misfires.
Later Revisions
BMW addressed many of the early reliability concerns in later versions, such as the S63TU, S63TU2 and S63TU4. BMW addressed many of the previous concerns in these technical updates, notably with the introduction of Valvetronic technology and higher compression ratios.
Tuning Potential of the S63 Engine
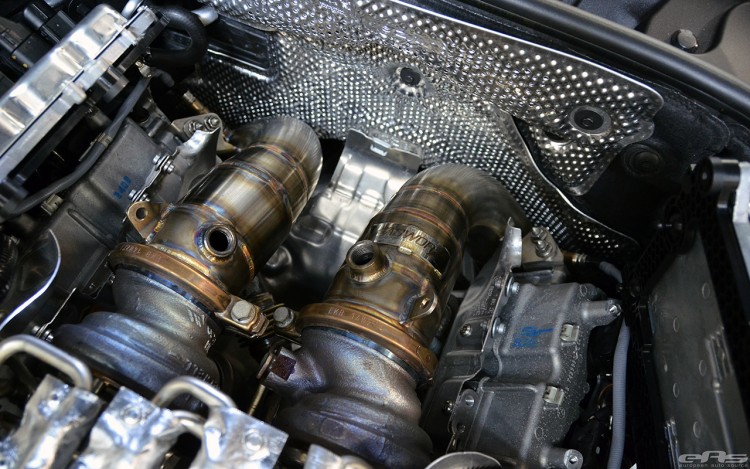

The BMW S63 V8 is a favorite among enthusiasts for its exceptional tuning potential. With its robust internals and advanced design, the engine can handle significant power increases when properly modified. Dyno tests have shown that the S63 produces far more torque at 1,500 rpm than the S85 V10 could muster at its peak!! Furthermore, it carries that locomotive like torque straight through to 5, 750 rpm. When it comes to power, the 535 horsepower in the F10 M5 S63B44T1 is fully delivered between 5,750-7,000 rpm sending the M5 to 60 mph in under 4 seconds using BMW’s new Launch Control. 0-124 mph takes a scant 13 seconds!
ECU Tuning
- Remapping the ECU can unlock substantial gains in horsepower and torque, with stage 1 tunes often adding 100+ horsepower.
- Custom tunes can optimize performance for specific setups, such as upgraded turbos or downpipes. We’ve seen tuners like G-Power achieving 740 horsepower in their F10 M5.
Hardware Upgrades

- Turbo Upgrades: Aftermarket turbos can significantly increase power output, with larger units capable of pushing the S63 beyond 1,000 horsepower.
- Exhaust Systems: High-flow downpipes and cat-back exhaust systems reduce backpressure and enhance performance and sound.
- Intercoolers: Upgraded intercoolers improve heat management, critical for maintaining performance during extended high-speed runs or track use.
- Fuel System Enhancements: High-flow fuel pumps and injectors ensure adequate fueling for larger turbos or aggressive tunes.
Strengthening Internals
- For those seeking extreme power levels, upgrading components like forged pistons, rods, and crankshafts can ensure the engine handles the increased stress.
- The drivetrain must also be upgraded to handle the increased power. Reinforced clutches, upgraded transmissions, and stronger differentials are often necessary for high-powered builds.
Efficiency
The BMW S63 engine combines impressive performance with relative efficiency for its class. Key features contributing to its efficiency include:
- Twin-Scroll Turbochargers: The use of twin-scroll turbochargers enhances low-end torque and reduces turbo lag, improving both performance and fuel economy.
- Valvetronic and Double-VANOS: BMW’s variable valve timing and lift systems optimize airflow and combustion, enhancing power delivery and efficiency across the rev range.
- Lightweight Construction: The aluminum block and heads reduce weight, improving overall vehicle efficiency.
- Fuel Economy: While fuel consumption is not the primary focus of an engine like the S63, models equipped with it often feature advanced engine management systems that balance power and efficiency, achieving reasonable mileage for a twin-turbocharged V8.
Which BMW Models Are Powered by the S63 Engine?
| Engine Code | Power & Torque | Models |
|---|---|---|
| S63B44O0 | 547 hp / 502 lb-ft (680 Nm) | 2010–2013 E70 X5 M 2010–2013 E71 X6 M 2011–2014 Wiesman GT MF5 |
| S63B44T0 | 553 hp / 502 lb-ft (680 Nm) | 2011–2017 F10 M5 2012–2018 F12/13 M6 2013–2018 F06 M6 Gran Coupe |
| S63B44T2 | 567 hp / 553 lb-ft (750 Nm) | 2015–2019 F85 X5 M 2015–2019 F86 X6 M |
| S63B44T4 | 591 hp / 553 lb-ft (750 Nm) | 2018–2023 F90 M5 2018–2023 F90 M5 Competition 2021 F90 M5 CS 2019–present F91/92/93 M8 2019–present F91/92 M8 Competition 2020–present F95 X5 M 2020–present F95 X5 M Competition 2020–present F96 X6 M 2020–present F96 X6 M Competition 2023–present Land Rover Range Rover Sport SV 2024–present Land Rover Defender OCTA |
First published by https://www.bmwblog.com
Source: BMW BLOG


